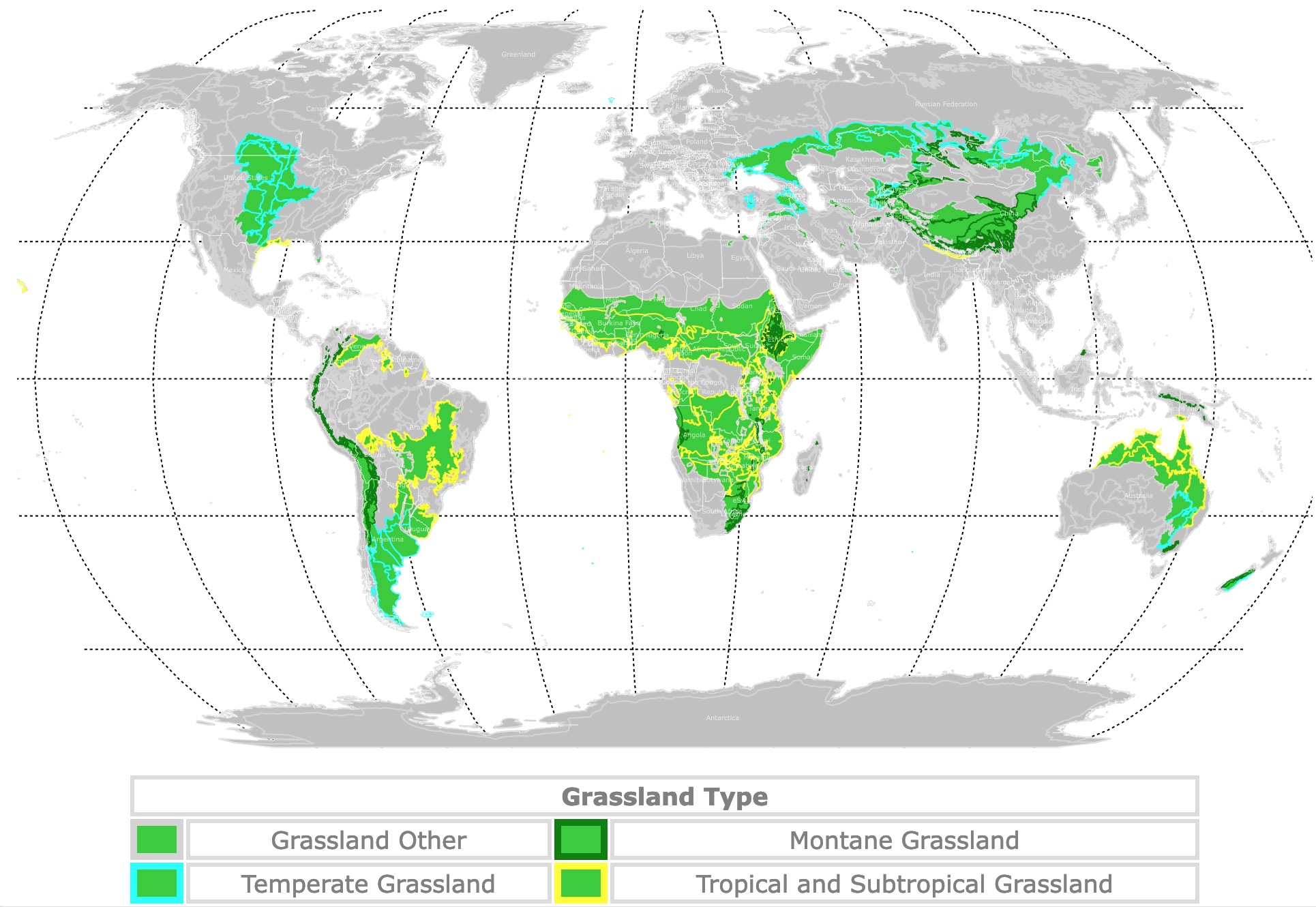
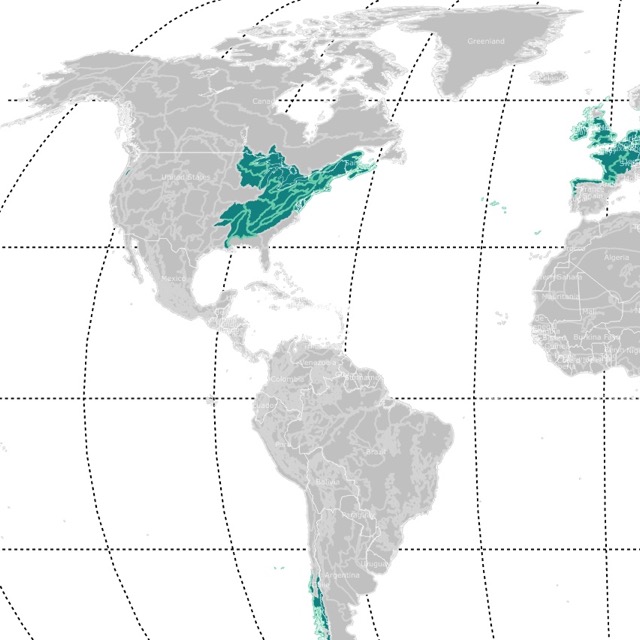
World Map of Grasslands
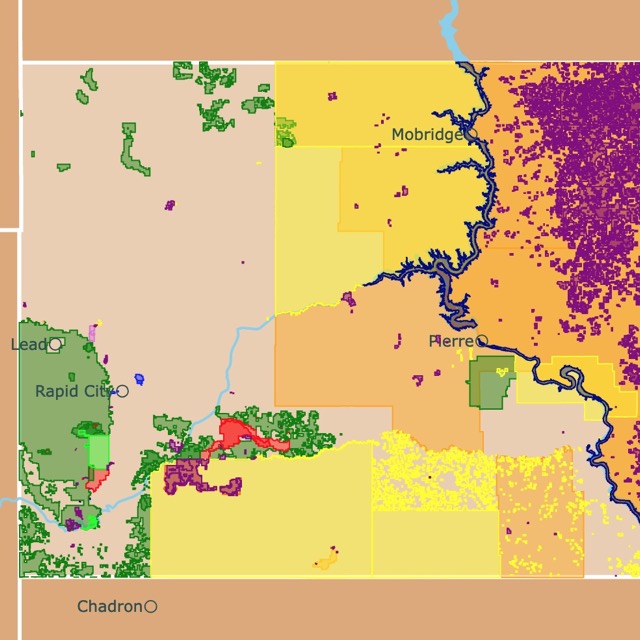
This map shows the world's Grassland Biome in green. Grassland types have borders in different colors. For more detail, hover over the map. To take a closer look, zoom in. For more information, scroll down.
| Grassland Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Grassland Other | Montane Grassland | ||
| Temperate Grassland | Tropical and Subtropical Grassland | ||
Grasslands
Grasslands are terrestrial habitats, open and continuous, usually covered by several grass species, flat or with gentle slopes. Different factors like soil, climate, and latitude, determine their presence.
Rain in Grasslands is enough for grasses to grow but not for trees or large shrubs to thrive. This is because rainfall is not regular but erratic. Most Grasslands have a rainy season and a dry season.

Uneven rains throughout the year make grasslands prone to draught and fires, inhibiting the growth of large trees. Fires and drought are essential for diversity. Some seeds will only grow after fires.
Trees may grow close to streams, but this is not the norm. Soils in grasslands may be thin, preventing large trees from establishing in this biome.
Grasses thrive in grasslands because their growing points are close to the ground. If there are fires and the top burns, they can grow back rapidly. In case of freezing or extreme drought, the roots and buds are protected and can grow again.
The same principle applies to grazing. Grasses can support high densities of grazing animals because being nibbled does not affect their growing points.
After the Pleistocene Ice Age, grasslands became more common when hotter and drier climates prevailed globally.
Grassland Locations
The Grassland biome can be found on all continents except Antarctica. Grasslands are widespread, but they can be found between temperate forests at high latitudes, near the interior of continents in mid-latitudes, and between deserts at lower latitudes.
Grassland Climate

On average, grasslands receive 20 to 30 inches (500 to 900mm) of rain per year. In comparison, deserts receive less than 11in (300mm) per year.
Temperatures in Grasslands vary significantly. Depending on the latitude, temperatures can range between -4°F (-20°C) and 86°F (30°C), NASA.
Grasslands are prone to human development. They are plowed to grow wheat and other crops, and wildlife is replaced with livestock. Unfortunately, few grasslands are protected.
Grassland Classification
Because of the range of locations, soils, and temperatures that affect grasslands, it is easier to describe them once they are classified.

Grasslands are broadly classified as Tropical Grasslands and Temperate Grasslands. But there are also grasslands at high altitudes. These are the Montane Grasslands which are also included on the map.
Temperate Grassland
Temperate Grasslands have hot summers and cold winters. Temperatures in temperate forests fluctuate more than in tropical grasslands. Average temperatures may range from 100°F (38°C) in the summer to -40°F (40°C) in winter.
Temperate Grasslands have no trees or shrubs, but some oaks, cottonwoods, and willows may grow along rivers.
There are two common Temperate Grasslands, Prairies and Steppes. A less common temperate grassland is the Pampas. These are present in southern South America.
Prairies
Prairies are found in North America, mainly in South Dakota, North Dakota, Nebraska, Montana, Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, Colorado, Wyoming, New Mexico, Alberta, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan.

Precipitation in Prairies is more common in late spring and early summer. Annual average precipitation is 20-35 inches (889 mm) per year.
The amount of rainfall affects the height of grasses. Tall grasses grow in wetter areas. Short grasses in drier areas.
When the settlers crossed the Mississippi River, they found tall grass of 11 feet (3.3m). The grass became shorter as they migrated to the west and drier areas.
The soil of the Prairies is dark, deep, and fertile. These nutrient-rich soils result from the decay of deep and branched roots.
Steppes
Steppes are more common in the interiors of Asia and Europe, especially in Ukraine and Russia. Still, there is also Steppe in North America.
Steppes are direr than Prairies. They average 10-20in (254-508 mm) rain per year.
Steppes usually have shorter grass than Prairies.
People use Steppes to grow wheat and feed livestock, UC Berkley.
Tropical Grasslands
Tropical Grasslands occur at lower latitudes. The most common form of Tropical Grassland is Savannas.
Savannas
The best-known Savannas are African. This is not just because of the large predators that roam these ecoregions but because they cover half of the African continent.

Savannas are also found in Australia and India. In South America, they are known as Llanos.
Because Savannas are tropical, they are always warm or hot.
The average rainfall in Savannas is 20 to 50in (510 to 1,270mm) per year. Savannas have a more pronounced seasonal drought. Rain is intensive half the year and almost null the rest of the year.
The soil in Savannas is porous and has fast drainage. Nevertheless, Savannas may have scattered trees.
Due to competition, soil, and rainfall, one grass type is predominant in each Savanna. Dry Savannas of the Serengeti have Rhodes grass and red oats grass. East African savannas have star grasses. Uganda has lemon grasses.
When rains come, grasses proliferate, and antelope calves are born to take advantage of the grass to feed on, UC Berkley.
Montane Grasslands
Montane Grasslands occur in high elevations, like montane or alpine areas.

These grasslands can be found in tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions.
Examples of these grasslands include the Tibetan Plateau in Asia, the Zambezian Montane Grasslands, the Ethiopian Highlands, and the montane areas of southeastern Africa.
Paramos are montane grasslands found in tropical South America, in countries like Colombia, Ecuador, Venezuela, and Peru.
Montane Grasslands have high species diversity because they are ecological islands due to altitudinal isolation.
This region has plants adapted to cold temperatures, intense sunlight, and wet conditions. These include rosette structures, hairs, and waxy surfaces. These plants can live at altitudes of 15,092 feet (4,600m). Source: ecologypocketguide.com.
Grassland Vegetation

- Prairies: Trees include Oaks, willows (close to rivers), and cottonwoods. Grasses include barley, salvia, oats, wheat, asters, blazing stars, coneflowers, sunflowers, wild indigos, goldenrods, clovers, buffalo grass, and psoralea.
- Steppes: Buffalo grass, sagebrush, speargrass, blue grama, cacti (America), and sunflower relatives.
- Savanna: Rhodes grass, red oats, star grass, lemongrass.
- Montane Grasslands: Lobelia (Africa), Cyathea (New Guinea), Puya (south America), Argyroxiphium (Hawaií), Aloe spp., Crassulaceae, and Ericoid thicket in (Madagascar).
Grassland Animals

- Prairies: Gray wolves, prairie dogs, coyotes, bobcats, foxes, wild turkey, flycatcher, Canadian geese, crickets, bison, jackrabbits, deer, mice, skunks, quails, badgers, owls, hawks, and sparrows.
- Steppe: hawks, snakes, badgers, owls.
- Savanna: giraffes, leopards, zebras, buffaloes, kangaroos (Australia)s, snakes, moles, termites, beetles, lions, hyenas, elephants, capibaras (South America).
- Montane Grasslands: Tibetan antelope, Tibetan wild donkey, Spectacled Bear (South America).
Resources for Grassland Biome Map
The shapefiles to create the map with ecoregions of the world were obtained from WWF. The shapefiles with the countries of the world were obtained from Natural Earth.
This map will be updated with new data! To receive updates on this and more nature maps, join my email list!!!!!!!
Made by Luz K. Molina with D3.js.