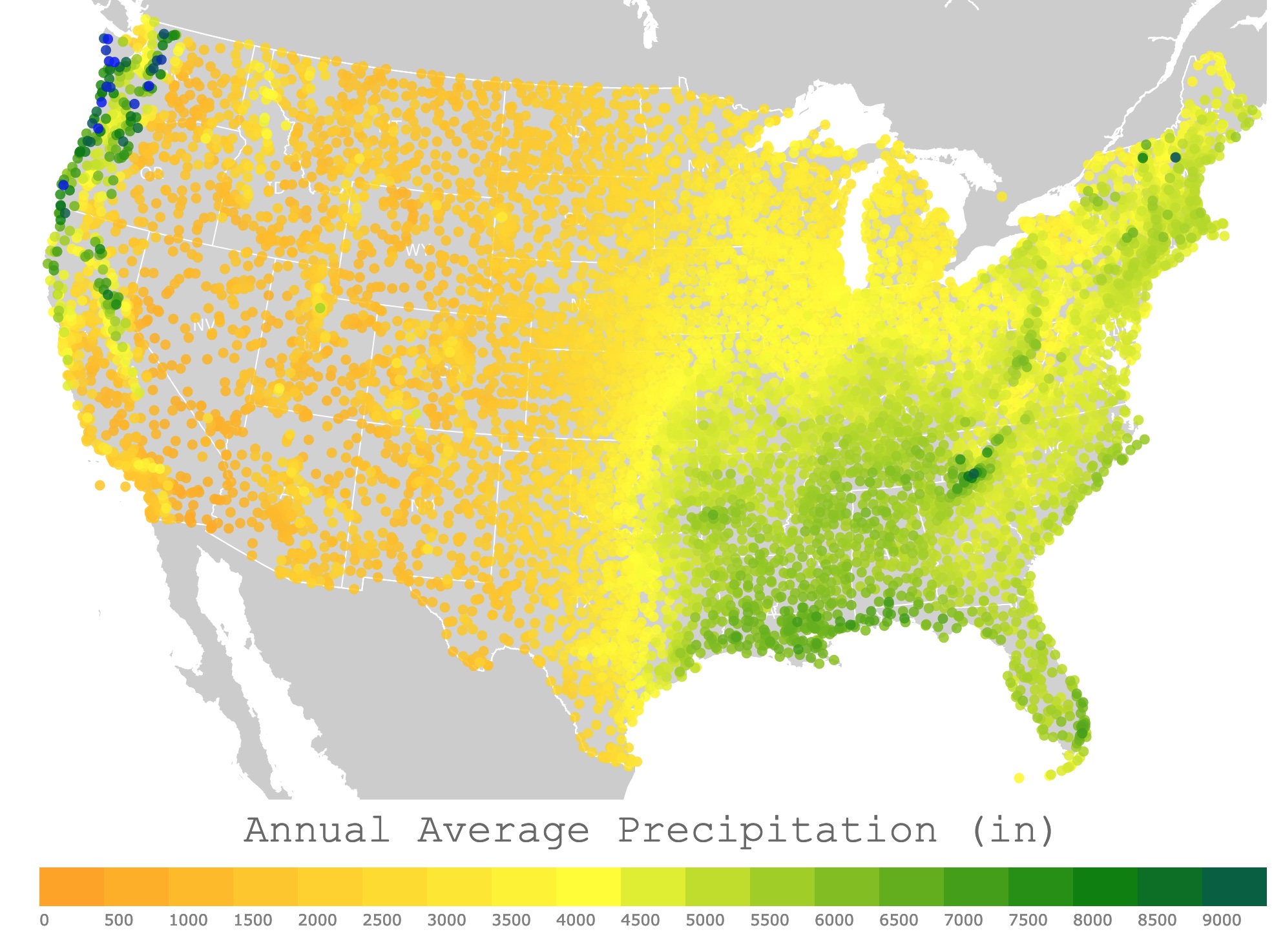
Map of Annual Precipitation in the U.S.A.
This interactive map displays the Annual Average Precipitation in the United States. For stations, precipitation, and elevation, hover over the map. Zoom out to see Alaska, Puerto Rico, and Hawaii. Zoom in to see all stations in detail.
Annual Average Precipitation (in)
Precipitation
Precipitation is water in its liquid or solid state that forms in the atmosphere and falls on Earth. It comes in different forms, like snow, hail, sleet, or rain.
Along with condensation and evaporation, precipitation is part of the global water cycle.
Precipitation forms when water vapor condenses in the clouds into bigger droplets of water. When the drops are heavy enough, they fall to the ground.
Most rain begins as snow. Clouds are high, where it is usually frigid. As the snowflakes fall through the warm air, they turn into raindrops.
Particles in the air provide a surface for the water droplets to condense. They are called "condenstion nuclei".
Precipitation is always fresh water. Even if the rain originates form the ocean. The reason is because that salt does not evaporate with the water; NatGeo.
Unfortunately, some atmospheric pollutants can dissolve in the water droplets before they fall onto Earth. An example of this is acid rain. It can dissolve stone sculptures, harm coral reefs n the ocean, and affect shells from aquatic organisms in aquatic environments.
If you love checking the weather, why not get your own weather station? Amazon has the Sainlogic WiFi Weather Station. You can experience the convenience of accessing all kinds of weather information directly at home. It is a 10.2-inch Large Display Wireless Weather Station. It comes with a Rain Gauge and a Wind Gauge.
Precipitation Types
There are different types of precipitation. The most known are rain and snow. Nevertheless, the temperature of the cloud, the ground, and the air between the two affects the type of precipitation.
Rain
Rain is made of liquid water droplets. It falls when the temperature in the air and the ground is above freezing (32°F, 0°C).
Rain can begin as water or ice crystals in a cloud, but it always falls as liquid water.
Hail
Hail is created inside thunderstorm clouds. Water droplets are pushed upward where temperatures are cooler.
The droplets freeze to form hailstones. These grow with more water droplets frozen to them, and they fall to the ground.
Hail can form big and heavy balls that can put dents in cars!
Sleet
Sleet is an icy precipitation that forms when the air between the cloud and the ground is warm. The cloud is on a layer below freezing temperatures, forming ice crystals. The ice melts as it falls through the warm layer of air.
The layer closer to the ground is below freezing, and the droplets freeze again forming sleet.
Freezing Rain
Freezing Rain starts like ice crystals that melt in the air turning into water droplets. If the layer just above the ground is below freezing, the water droplets will freeze as they land.
Graupel
Graupel could be described as a type of snow.
Graupel forms in temperatures below freezing, where snow crystals in the clouds get in contact with cold water droplets.
The water freezes over the snow, giving graupel a slushy appearance; SciJinks
Snow
Snow falls when all the air between the cloud and the ground is below freezing.
Looking at snowflakes closely, you will see the crystal formations that make them unique.
If you would like a creative way to check the weather, Amazon has the Weather Storm Glass Bottle. This decorative glass container comes with a transparent solution. Depending on the temperature, crystals will form different shapes.
Factors that Affect Precipitation
The main factors affecting precipitation are prevailing wind, mountain ranges, and seasonal winds.
Prevailing Winds
These are the winds that are predominant and come from a particular place or season. Prevailing winds are carry warm, moist, or cool air over land.
The amount of water vapor in the air mass influences the amount of precipitation.
Winds from water bodies carry more moisture than those that blow over land.
Mountain Ranges
A mountain range is a line of mountains connected by high ground. A mountain range in the path of prevailing winds affects where precipitation will fall.
As humid winds from the ocean blow toward mountains, they are forced to rise. As they rise, they cool and condense. This results in rainfall or snowfall on the windward side of the mountain range.
When the air moves over the mountain, it is cool and dry. There is little precipitation on this side. This is the leeward side of the mountain range. This is what is commonly called a rain shadow.
Rain shadows are dry arid areas known as deserts.
Seasonal Winds
Winds that blow during a particular season are called seasonal wind.
Changes in seasonal wind affect precipitation.
Seasonal winds are like land or sea breezes. The sea and land breezes that cover an extensive area and change direction, are called monsoons. Monsoons are common in Asia.
Precipitation in the U.S.A.
The precipitation shown in this map is the annual average total for each station depicted. The averages were calculated between the years of 1981 and 2010. The data comes from 9,308 stations in the U.S.A. and its territories.

Precipitation was measured with different rain gauges. The annual average is displayed in inches. The elevation of each station is in meters above sea level. To learn more about the data, check this article from NOAA.
Extreme Precipitation Locations in the U.S.A.
The table below displays the rainiest and driest places in the United States and the conterminous U.S.
Because the 5 rainiest places in the U.S. are outside the conterminous United States, I decided to also include the 5 rainiest places in the lower 50 states.
| Precipitation (inches) | State/Territory | Station | Elevation |
| 236 | California | DEATH VALLEY | -59.1 |
| 259 | California | CALEXICO 2 NE | 3.7 |
| 278 | California | BRAWLEY 2 SW | -30.5 |
| 285 | California | EL CENTRO 2 SSW | -9.1 |
| 288 | California | NILAND | -18.3 |
| 11790 | Oregon | PORT ORFORD 5 E | 45.7 |
| 11830 | Washington | RAINIER PARADISE RS | 1654.1 |
| 11888 | Oregon | NEHALEM 9 NE | 42.7 |
| 11972 | Washington | FORKS 1 E | 106.7 |
| 12228 | Oregon | LAUREL MTN | 1093.9 |
| 21392 | American Samoa | AASUFOU | 408.4 |
| 21416 | Federated States of Micronesia | PAIES-KITTI | 45.7 |
| 21460 | Alaska | WHITTIER | 18.3 |
| 23659 | AK | LITTLE PORT WALTER | 4.3 |
| 24002 | Hawaii | GLENWOOD NO. 2 55.4 | 670.6 |
The driest places in the U.S.A. are in California. The driest place is Death Valley, with an annual average precipitation of 236 inches. Death Valley is a desert and the hottest place on Earth, with temperatures that have reached 134.1°F (56.7°C).
The valley is very arid because it lies in the rain shadow of four major mountain ranges, including the Sierra Nevada and Panamint Range.
The rainiest place in the U.S. is Glenwood, Hawai'i. Hawai'i is quite rainy in some areas thanks to the mountains that trap the trade winds that move from the Pacific Ocean.
The second rainiest place is Whittier, Alaska.
In the conterminous United States, the rainiest place is Forks, Washington.
Resources for U.S. Precipitation Map
The snowfall averages were downloaded from Anthony Arguez, Imke Durre, Scott Applequist, Mike Squires, Russell Vose, Xungang Yin, and Rocky Bilotta (2010). NOAA's U.S. Climate Normals (1981-2010). [Snow-Inventory]. NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. DOI:10.7289/V5PN93JP [November 2022].
The Shapefiles for this map were downloaded from Natural Earth.
Made by Luz K. Molina with D3.js.
This map will be updated with improved and recent information! To receive updates on this and more nature maps, join my email list!!!!!!!