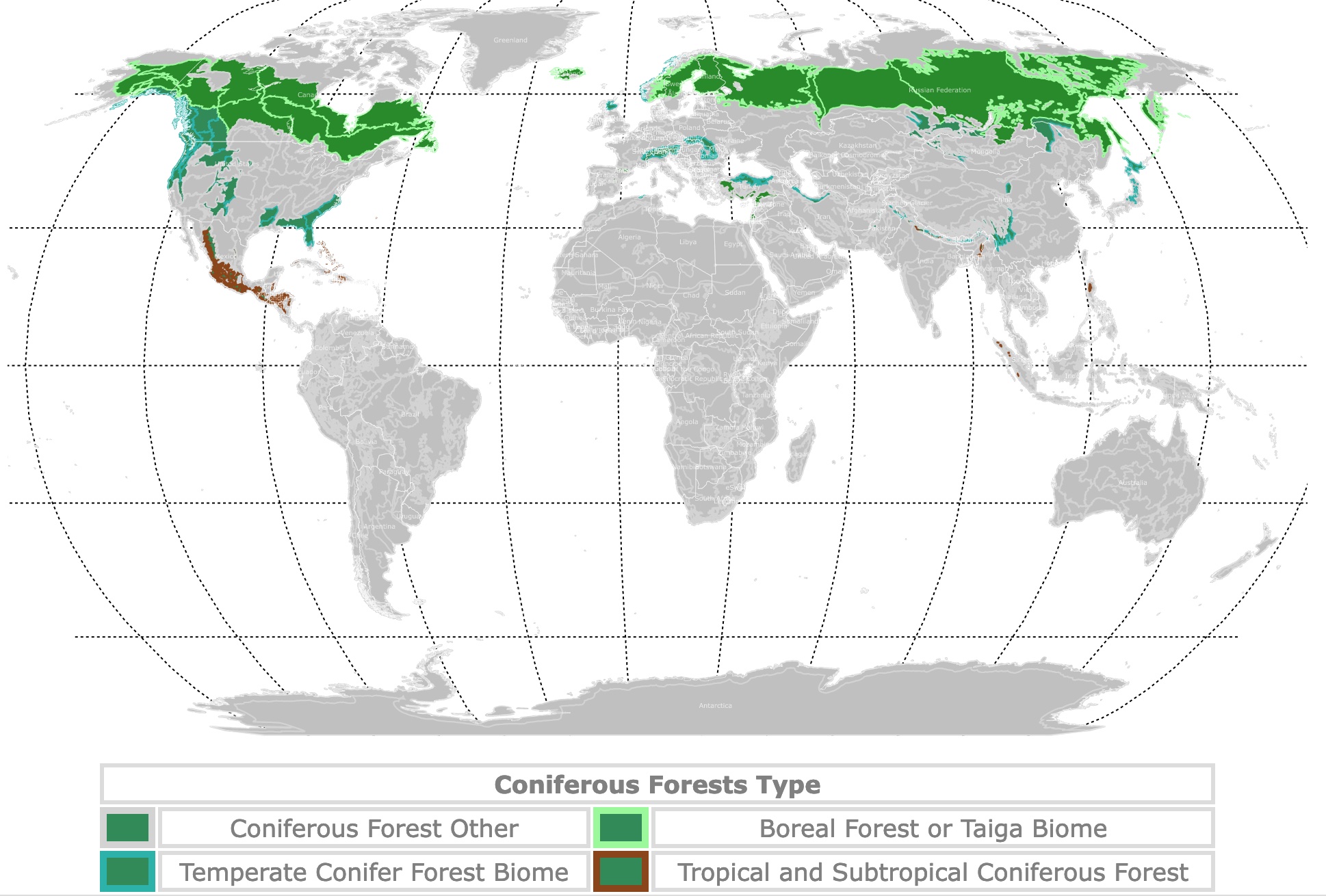
World Map of Coniferous Forests
This map shows the world's Coniferous Forests in green. Coniferous Forest types have borders in different colors. For more detail, hover over the map. To take a closer look, zoom in. For more information, scroll down.
| Coniferous Forests Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Coniferous Forest Other | Boreal Forest or Taiga Biome | ||
| Temperate Conifer Forest Biome | Tropical and Subtropical Coniferous Forest | ||
Coniferous Forests
Coniferous Forests are forests that are dominated by trees with needles and bear cones.
Conifer trees belong to the group of plants called Gymnosperms. This means they have cones and do not have flowers and fruits like the Angiosperms.
Coniferous trees are sometimes called softwoods because they can stand cold temperatures and acidic soils. Softwoods are slightly softer than hardwoods.
Softwoods are more commonly used for construction, paper pulp, and card products.
Conifers are specialized in poor and acidic soils that are often sandier than those found in deciduous forests.
Conifer forests succeed in poor soils because they grow slowly and die old. Instead of producing new leaves each spring, they keep and care for their existing needles and keep them for many years, Untamed Science.

Conifer trees' characteristics help them stand cold weather. For example:
- Conical Shape: helps with snow shedding and preventing branch losses.
- Needleleaf: these narrow leaves reduce the surface area, therefore reducing transpiration. Saving water is important because water is not available since it is in the form of ice.
- Thick Waxy Cuticles: protect stomata (leaf pores) from drying winds.
- Evergreen: keeping the needles helps trees start photosynthesis as soon as temperatures are above freezing.
- Dark Color: to absorb the most heat and light from the sun.
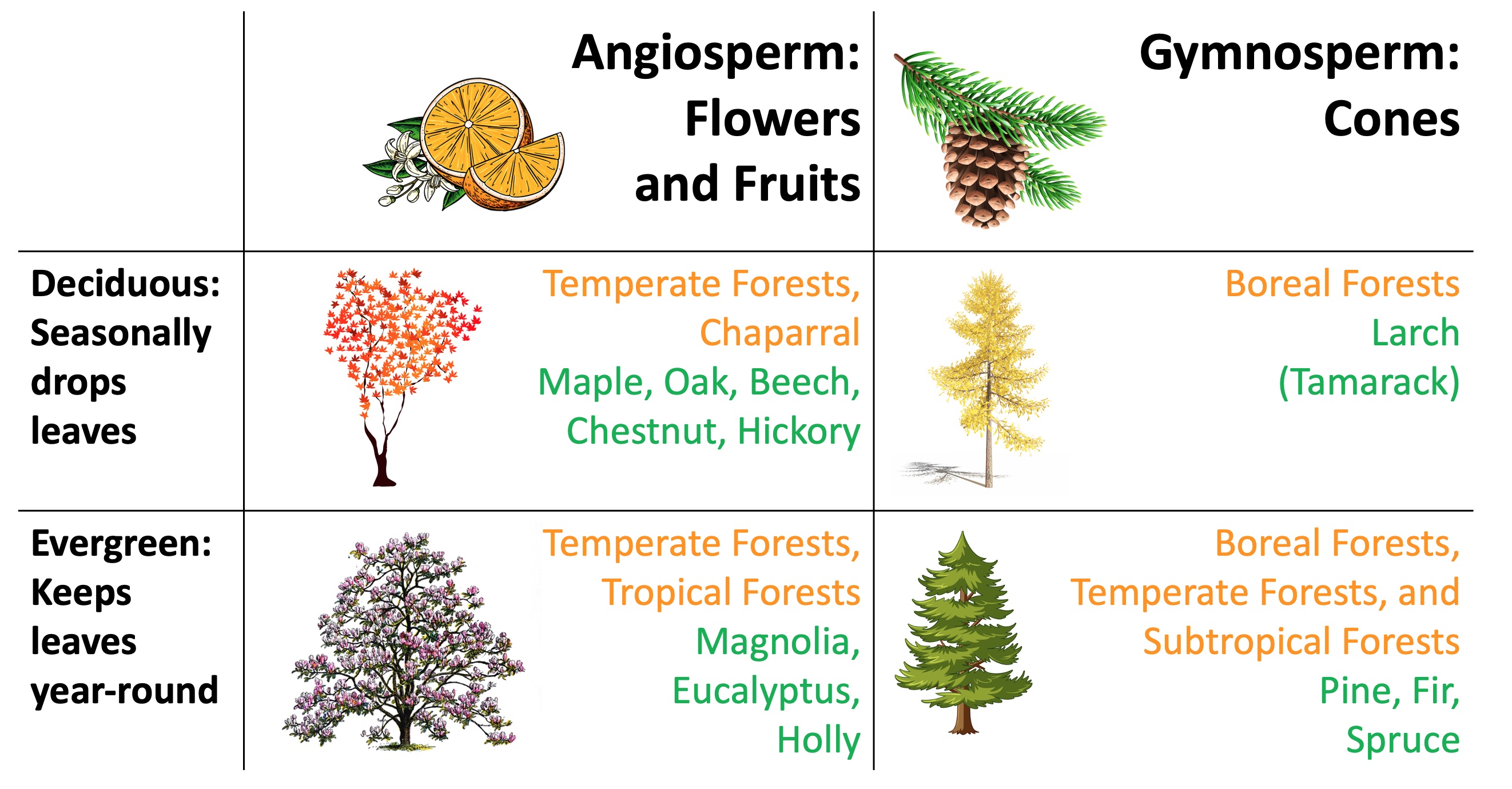
Even though most conifers are evergreen, there are some groups that are not evergreen.
For example larch, also called Tamarack (Larix spp.), is a conifer tree that is also deciduous (loses its pine needles in the fall).
Before describing and explaining Coniferous Forests in-depth, it is essential to separate them according to the biome where they live.

Biomes are significant communities of plants and animals that occupy a distinct region. They are characterized by abiotic factors like temperature, precipitation, sunlight, or pH.
Conifers are found in the Broadleaf Deciduous Mixed Forest Biome along with deciduous trees, hence the name Mixed. Nevertheless, these forests are not Coniferous Forests.
Conifers are dominant in the Boreal Forest Biome, Temperate Conifer Forest Biome, and Tropical and Subtropical Coniferous Forest Biome, therefore Coniferous Forests.
For a deeper undertanding of conifers, Amazon has Conifers: The Illustrated Encyclopedia. This encyclopedia includes the latest cultivars but also rarities. From towering redwoods photographed in their coastal habitat to recent dwarf varieties so popular in small gardens, conifers are presented in all their astonishing diversity.
Boreal Forests or Taiga Biome
Boreal Forests are also known as Taiga or Snow Forests. Boreal Forests cover up to 11% of the world's landmass. Hence they are the world's largest biome!

Boreal is used to describe the southern part of the biome, while Taiga is used to describe the northern part.
Boreal Forests have many freshwater bodies like rivers, lakes, marshes, and bogs.
Boreal Forests Location
Boreal Forests are in the Northern Hemisphere, between the latitudes 50°N and 65°N. They are an almost continuous belt of coniferous forests across North America and Eurasia.
They are mainly found in northern Asia, Europe, Canada, and Alaska.
Taiga is over former glaciated areas and areas of patchy permafrost on both continents.
The Biome north of the Boreal Forest is the Tundra Biome.
Boreal Forests Climate

Taiga has long winters of up to six months with mean temperatures below freezing. Winter average temperatures generally stay around -4°F (-20° C).
Summers are short, with 50 to 100 frost-free days in which the vegetation grows. The average summer temperatures are around 50°F (10°C).
Nevertheless, there is a wide range of temperatures in these forests. For example, Verkhoyansk, Russia, has recorded extremes of -90°F (-67°C) and plus 90°F (32°C).
Mean annual precipitation is 15 to 20 inches (381 to 508mm), but with low evaporation rates, the climate is humid, Radford.
Boreal Forest Vegetation
Just a few species of conifers are common in Boreal Forests. They are the evergreen spruce (Picea), pine (Pinus), fir (Abies), and the deciduous larch or tamarack (Larix) that grows in the northern Boreal Forest.
Boreal Forest Fauna
Animals commonly found in Boreal forests include:
- Predators: Lynx, weasels like mink, fishers, and sable, black bears, and grizzly bears
- Herbivores: hare, squirrel, lemmings, elk, moose, and beaver.
- Birds: warblers, finches, sparrows, and ravens.
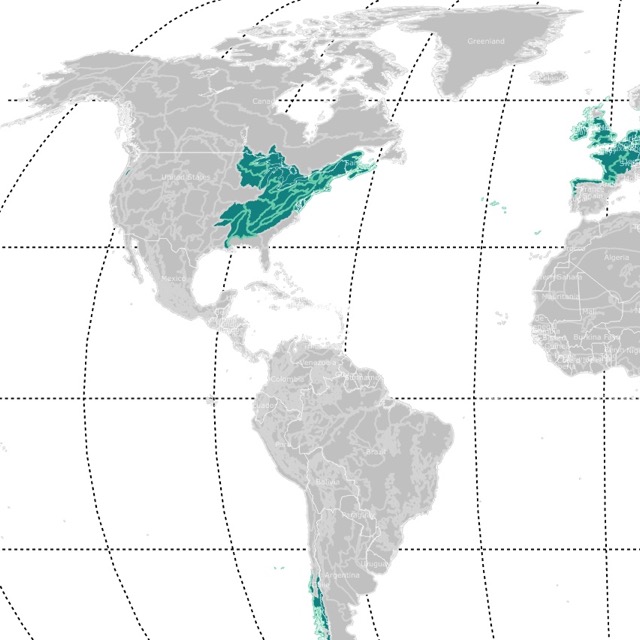
Temperate Conifer Forests
Temperate Conifer Forests are found in coastal areas with mild winters or inland montane regions with drier climates.

Temperate Conifer Forests sustain the highest levels of biomass among terrestrial ecosystems. This is thanks to the massive size of some of its trees.
For example, the forests of northern California have the giant sequoia (Sequoiadendron gigantea), which is the largest tree worldwide. They also have the coastal redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), which may reach heights of 328ft (>100m), therefore the tallest tree in the world.
These forests are usually structured into two layers. An overstory and an understory. Some may support a layer of shrubs. Source: ecologypocketguide.com
Temperate Conifer Forest Location
Temperate Conifer Forests are found in European countries like Austria, Norway, the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland, Poland, Romania, Ukraine, Czech Republic, and Slovakia.
They are found in Russia, China, Japan, and Mongolia in Asia.

In North America, they are found in the West Coast in British Columbia, California, Alaska, Washington, and Oregon.
They are found on the Rocky Mountains in Idaho, Montana, and Wyoming.
They are found Nevada, Utah, Texas, Colorado, and Arizonain the South West.
Temperate Conifer forests are also found in Arkansas, New Jersey, and Virginia.
Finally, they are found in southern states like North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama.
To learn more about temperate coniferous forests Amazon has Native and Ornamental Conifers in the Pacific Northwest: Identification, Botany and Natural History. This book presents an integrated perspective for understanding and identifying conifers in any landscape where native and ornamental species grow alongside each other. It is suitable for landscape designers, horticulturalists, arborists, gardeners, environmental scientists, and botanists.
Temperate Conifer Forest Climate
Temperate Conifer Forests have warm summers and cool winters. The temperature varies widely depending on location.
Precipitation in these forests also depends on location, but it is about 12-35in (300-900mm). Some areas can have up to 78in (2,000mm) of rain a year.

Temperate Conifer Forest Vegetation
Common tree species include douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga spp.), pine (Pinus spp.), cedar (Juniperus spp., Cupressus spp., Thuja spp.), fir (Abies spp.), and redwood (Sequoia spp.).
There are also lodgepole pines, black and white spruce, jack pine, and balsam fir (commonly used as Christmas tree). Common in Europe and Asia, the Yew tree can live for thousands of years and is poisonous.
The bottom herbaceous layer is comprises grasses, ferns, and forbs.
Some of the plants on this layer include Saskatoon berry, Salal, Nootka rose, Pitcher Plants, Sword ferns, licorice ferns, thimbleberry, sword ferns, reindeer moss, and plume moss.
Temperate Conifer Forest Fauna

The herbivorous organisms that live in these forests must be capable of digesting acid plants.
Another common feature is that these organisms are adapted to cold temperatures. Most of them are warm-blooded, have warm coats, and some of them hibernate or migrate during winter.
Examples include Nematodes (roundworms that decompose matter), mosquitoes (found on stagnant water in all coniferous forests), bark beetles, moths, and amphibians.
Frogs, toads, and salamanders are quite common in moist areas.
Canada geese are known to migrate and are found all over North America, and crossbill, whos beak is adapted to feed on cone seeds.
Mammals include mice, squirrels, chipmunks, bears, beavers, chamois (similar to a goat), and wolverines. Source: Conserve Energy.
Tropical and Subtropical Coniferous Forests
Tropical Coniferous Forests support more than 200 species of conifers.
Most of these forests have only one layer. The trees are so thick and block so much light that usually only ferns, fungi, and bryophytes grow below.
Tropical and Subtropical Coniferous Forests Location

Tropical coniferous forests are found in the Philippines, Indonesia, the Bahamas, Central America, Mexico, Cuba, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic.
Tropical Coniferous Forests Climate
These forests don't have much temperature variability.
The average temperature year-round is 64°F (18°C).
Precipitation is higher than in the previous conifer forests. It can amount to 2.4in (60mm) or more in a month!
Vegetation of Tropical Coniferous Forests
Mexico has the richest and most complex tropical coniferous forest, while Cuba, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic have a lot of endemic (found only in these places) conifers.
Tropical Coniferous Forests Fauna
These forests support larger carnivores like mountain lions, cougars, coyotes, bobcats, and wolves.
Other animals include owls, white-tailed deer, gray foxes, brown-headed cowbird, black-tailed jackrabbit, and monarch butterflies!
It is important to highlight that many animals in these forests are sensitive to logging and fragmentation.
Coniferous Forests Considerations
Due to climate change, it is expected that by the end of the 21st century, most coniferous forests and temperate broadleaf forests will migrate to the poles. This will promote fragmentation and migration of animals with them.
Fires are essential for temperate coniferous forests. Forests are usually dominated by few plants. When they burn, the area is cleared for diverse species to colonize it.
Some seeds only grow after a fire.
Many of these forests have been reduced due to logging for lumber and land clearing for agriculture. Temperate coniferous forests are also close to industrialized areas and cities, wich results in more forests loss.
Coniferous forests need our help and protection to be around a lot longer!
Resources for Coniferous Forest Biome Map
The shapefiles to create the map with ecoregions of the world were obtained from WWF. The shapefiles with the countries of the world were obtained from Natural Earth.
This map will be updated with new data! To receive updates on this and more nature maps, join my email list!!!!!!!
Made by Luz K. Molina with D3.js.